Start your homelab journey using docker
What is Docker
Docker is an open-source platform that allows developers to easily develop, deploy, and run applications in containers. It enables software to be packaged into a portable and lightweight container that can run on any system regardless of its infrastructure.
A container is an isolated environment that contains everything an application needs to run, such as libraries, dependencies, and the code itself. Docker containers are lightweight, fast, and efficient, and they can be easily moved from one environment to another, making them an ideal choice for modern application deployment.
The main advantage of Docker is that it allows developers to create applications that can run consistently across different environments, from development to production. This is achieved through containerization, which ensures that the application environment is consistent, regardless of the underlying infrastructure.
How is a container different from a virtual machine?
Containers are an abstraction at the app layer that packages the code and dependencies. On the other hand, Virtual Machines are an abstraction of the physical hardware. This means that Virtual Machines can turn one server into multiple servers and containers can take advantage of the software in the virtual machine and create multiple containers. This is like inception, a service within the server within the virtual server. This makes it great for starting up and migrating of the microservices really quick.
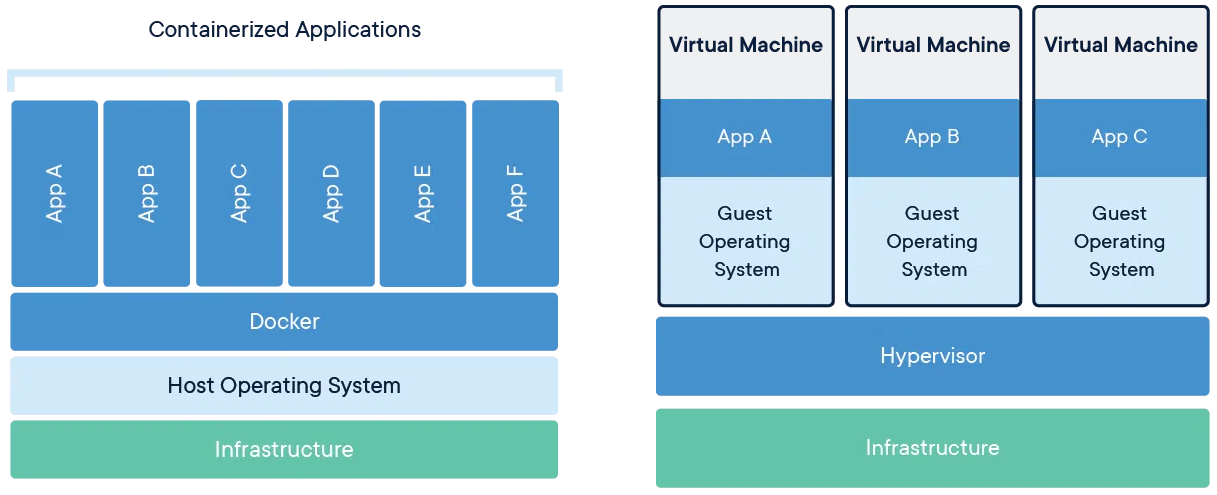
The Beauty of Docker is that it can also run on many OS, from Windows to MacOS and Linux. You have no boundaries and the services will run the same way.
How to install Docker
Now that you understand docker a little more, let’s get into how to get started with docker.
Whether you’re using Windows or Linux, steps are very similar.
Windows Install
Before starting to install Docker for Windows, it is important that you know that you will need to install Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL 2).You will also need to download the Docker Desktop for Windows.
Installing Windows Subsystem for Linux
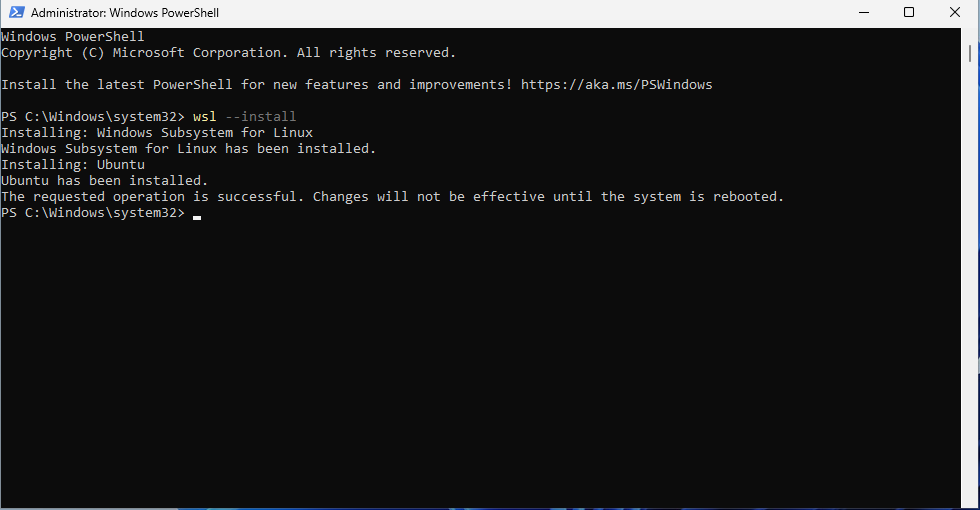
First, you will need to open PowerShell as administrator and run the following command. wsl --install
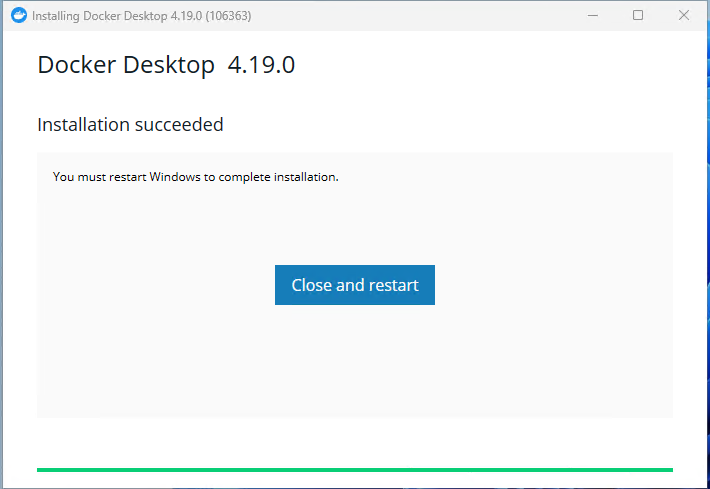
Go ahead and restart your computer and then install the Docker Desktop for Windows App.Let the installer load and click on Okay
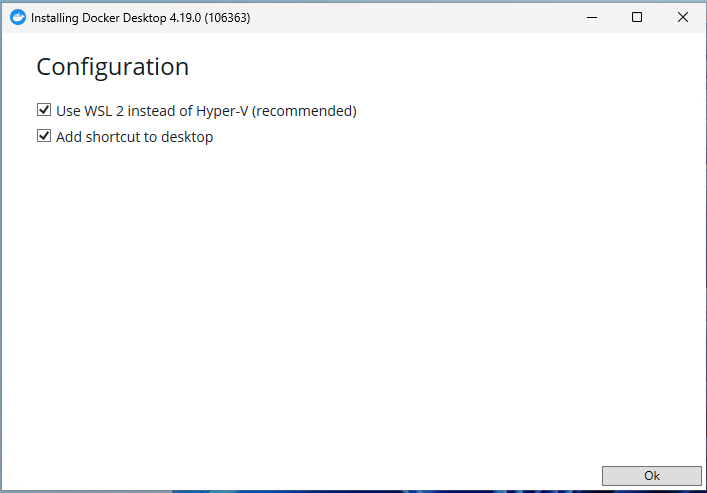
The installer will do its thing and then you will be prompted to restart one more time
Linux Install
Installing Docker on a Linux distribution is pretty straight forward.
- First, we would want to run a update of the configured sources.
Runsudo apt updateorsudo apt-get updatedepending on your linux distribution. - Then we will need to run
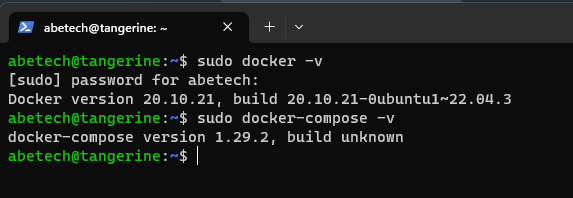
sudo apt install docker.ioas well assudo apt install docker-compose - Verify that this has been successfully installed by running the following command:
sudo docker -vorsudo docker-compose -vand it should return your docker version.
Final remarks
Docker is a useful tool to deploy containerized applications and it is very straight forward to install. There are many applications that can be deployed using Docker, from databases like MariaDB, mySQL and more to applications like NextCloud, Bitwarden, nginx, Ghost and many many more.
On our next guide, I will walk you through how to deploy Docker applications and deploying a Docker management tool, called Portainer, using Docker.
If you enjoy the content, please consider subscribing as it helps grow the blog!





